The PEMAC Body of Knowledge
Overview
The Asset Lifecycle
The figure below illustrates the relationship between the "Whole Life" perspective and the "Active Life" perspective of an organization's assets. The phrase "Asset Management" generally refers to this "Whole Life" perspective. Maintenance Management, if handled correctly, consists of activities and touch points across the whole life cycle. That said, most Maintenance Managers spend their days working with assets that are in their "Active Life" phase.
 In terms of the life-cycle costs for an asset, some portion is spent in its selection, design and construction and another is incurred during the active phase, namely operating and maintenance costs. Though not always applied wisely, the adage, "you get what you pay for" expresses that there is a relationship between what you invest up front and the subsequent costs related to operations and maintenance of an asset. "Whole life" costs are inescapably determined on design and purchase decisions but whether the minimum whole-life cost is achieved depends heavily on the discipline with which the asset is operated and maintained in its "Active life" stage. Different systems and competencies are required to manage each phase of the lifecycle, and for large scale assets it becomes a particular challenge to achieve a healthy transfer of relevant information between those responsible for the various functions.
In terms of the life-cycle costs for an asset, some portion is spent in its selection, design and construction and another is incurred during the active phase, namely operating and maintenance costs. Though not always applied wisely, the adage, "you get what you pay for" expresses that there is a relationship between what you invest up front and the subsequent costs related to operations and maintenance of an asset. "Whole life" costs are inescapably determined on design and purchase decisions but whether the minimum whole-life cost is achieved depends heavily on the discipline with which the asset is operated and maintained in its "Active life" stage. Different systems and competencies are required to manage each phase of the lifecycle, and for large scale assets it becomes a particular challenge to achieve a healthy transfer of relevant information between those responsible for the various functions.
Asset Management
ISO 55000 defines asset management as:
The set of coordinated activities that an organization uses to realize value from assets in the delivery of its outcomes and objectives. Realization of value requires the achievement of a balance of costs, risks and benefits, often over different timescales.
and advocates that an integrated management system across the entire life cycle of assets is required to support effective decision making at every phase.
The basic subject elements of such a system have been described in the GFMAM Asset Management Landscape and are diagrammed in the model below. Many of our members are working to develop Asset Management management systems and have been sharing their insights. We are using these subject groupings to tag and categorize this shared learning.
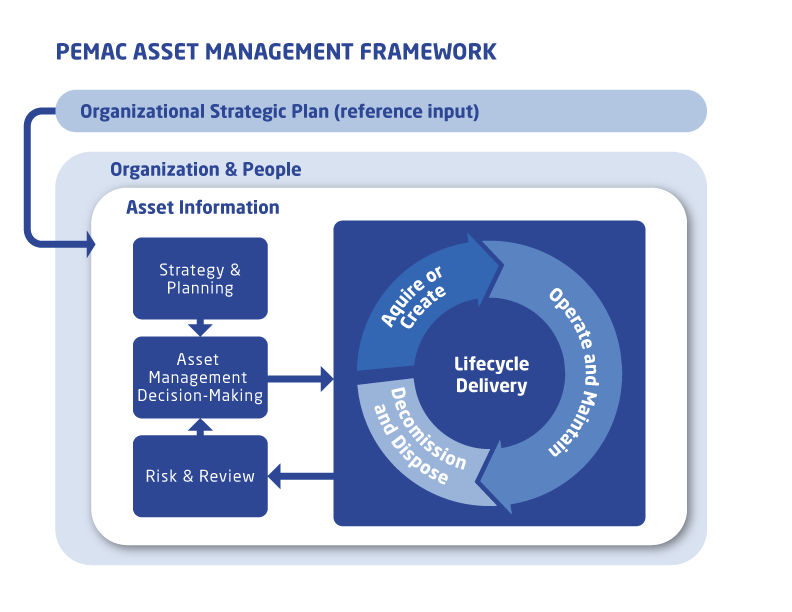
Maintenance Management
The PEMAC founders identified that those working in the "Active Life" phase of the asset life cycle have a key, and often overlooked, contribution to make to their organization's mission in terms of achieving the intended costs, risks and benefits from its physical assets. They believed that organizations would reap significant rewards in terms of reduced risk, improved safety and improved performance if maintenance managers were equipped with the ability to develop a strategic approach to maintenance management and to articulate problems and solutions in business terms. Thus, the majority of our members work in the active life portion, or the "Operate & Maintain" phase of the asset life cycle.
Within the GFMAM Asset Management Landscape, the Maintenance Management function is largely covered under the subject of "Maintenance Delivery" within "Lifecycle Delivery" subject grouping. The Maintenance Management framework, below, is essentially a 'zoomed in' look at the Maintenance Delivery subject that allows us to break down the PEMAC Body of Knowledge content more usefully with reference to well-known strategies and tactics, while also showing important linkages to the overall business and asset management context.
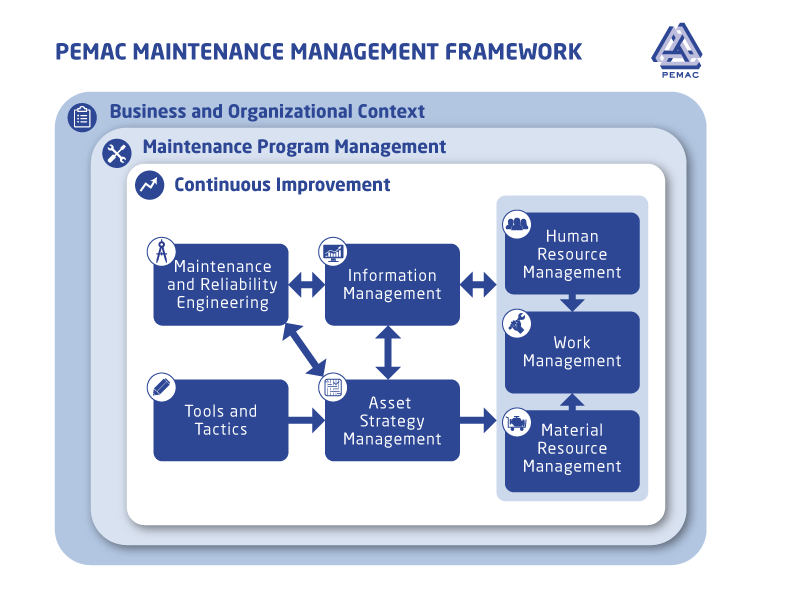
The Relationship Between Asset Management and Maintenance Management
We hope it's clear that Maintenance Management topics are all covered within "Asset Management". Maintenance Management is a vitally important subset of Asset Management. It is not the only subset, but it is the one in which PEMAC members are actively developing expertise. So even though the Asset Management subjects are all-inclusive, we have created the Maintenance Management framework to 'zoom in', while reminding ourselves constantly about how it aligns with overall business objectives.
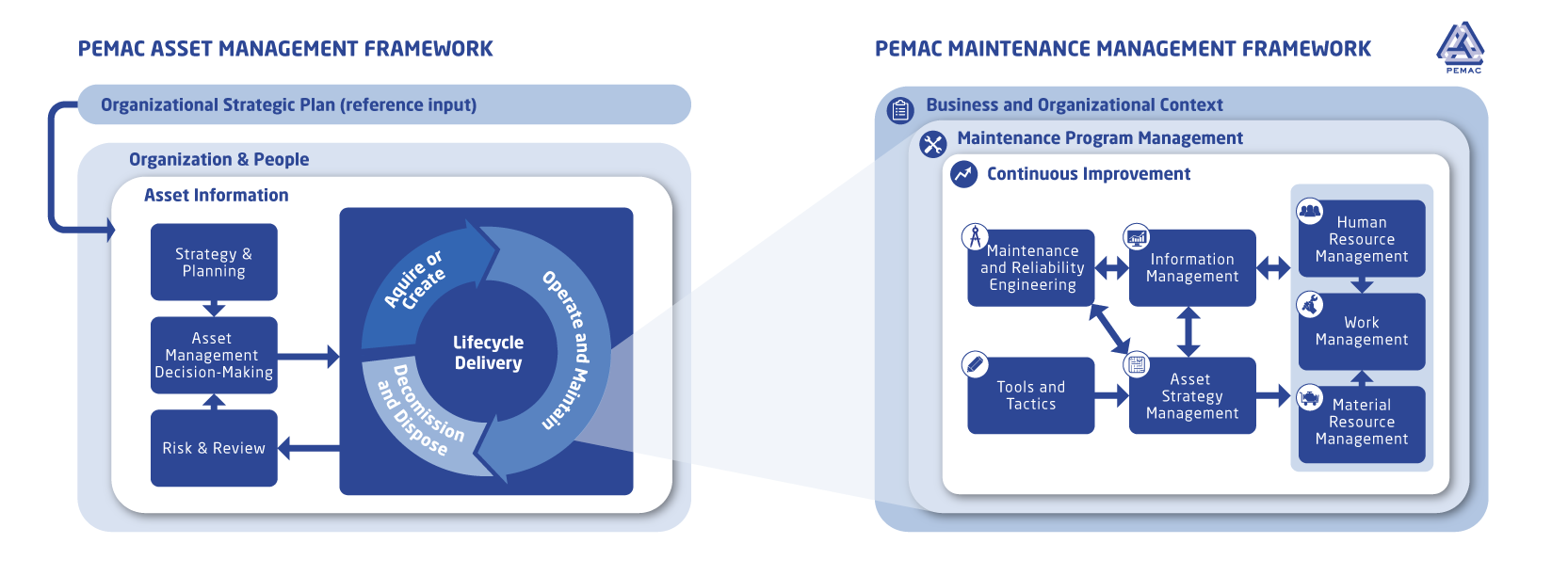
Search the Shared Learning Library >>


